As businesses continue to adopt digital-first strategies, the need to connect tools, automate workflows, and streamline data processes has never been greater. Yet, traditional software development often demands specialized skills, long deployment cycles, and heavy IT dependencies. That’s where a low code integration platform comes in — bridging the gap between technical and non-technical users by simplifying how applications, data, and systems interact.
Low-code integration platforms allow users to connect multiple systems, design workflows, and deploy automation solutions without extensive coding. With intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces, pre-built connectors, and real-time automation capabilities, teams can accelerate innovation while reducing manual work. From marketing and HR to IT and operations, these platforms empower teams to automate processes efficiently and maintain control over their data.
Open-source tools like Baserow are at the forefront of this movement. By combining flexible data modeling with user-friendly design, Baserow enables organizations to build internal tools and integrations that adapt to their specific needs — all without writing complex code. Whether you’re a startup managing customer data or an enterprise synchronizing multiple databases, Baserow provides a foundation for building connected, automated systems that scale.
Understanding Low-Code Integration Platforms
A low-code integration platform is a development environment designed to help users build and connect applications using minimal hand-coding. Instead of manually writing integration scripts, teams can rely on visual workflows, reusable logic blocks, and automation triggers to link different applications and data systems.
These development platforms are crucial for organizations managing multiple software tools that need to “talk” to one another — from CRMs and ERPs to analytics dashboards and cloud services. With pre-built connectors, businesses can easily automate data transfer between apps, handle real-time updates, and reduce human error in repetitive tasks.
According to Gartner’s definition, low-code application platforms are designed to accelerate application delivery by reducing complexity through visual development environments. This simplicity is particularly useful for teams with mixed expertise, where both developers and non-developers can collaborate effectively.
Low-code integration is not just about automation — it’s also about adaptability. As companies scale, they face increasing demands for business process automation, regulatory compliance, and cross-platform connectivity. By using low-code tools, teams can respond quickly to business needs, integrating cloud storage, marketing tools, customer databases, and internal analytics systems in just a few clicks.
You can learn more about the broader low-code and no-code ecosystem and key features in this related post: Low-Code vs. No-Code Platforms, which explores how these approaches are reshaping modern software creation.
Benefits of Low-Code Integration for Businesses
.png)
- Faster Application Development
Traditional application development cycles can take months, but low-code integration platforms significantly reduce that timeline. Teams can visually map out automation, set triggers, and connect systems without waiting for complex backend coding. This leads to faster prototyping, testing, and deployment, giving organizations a competitive edge.
By offering user-friendly interfaces, low-code platforms make innovation accessible to everyone — not just developers. A marketing manager, for example, can design an automated reporting workflow without IT intervention, saving valuable time and resources.
- Empowering Technical and Non-Technical Teams
Low-code tools bridge the divide between technical and non-technical users. Business teams can build automations independently, while developers focus on more strategic or complex tasks. This empowerment drives efficiency and encourages cross-functional collaboration.
For example, an operations manager can use a platform like Baserow to integrate CRM data with supply chain updates — ensuring everyone in the organization is working with synchronized, accurate information.
- Cost Efficiency and Resource Optimization
Reducing the dependency on dedicated developers translates to lower operational costs. By leveraging pre-built connectors and automation templates, companies can implement solutions faster and with fewer resources. Moreover, these platforms reduce human error by automating repetitive tasks, leading to better consistency and reliability.
Many small and mid-sized businesses choose open-source tools like Baserow because they combine flexibility with cost savings — allowing users to self-host or integrate the platform with their existing systems without licensing limitations.
- Business Process and Workflow Efficiency
Business process is one of the biggest advantages of low-code integration platforms. By simplifying everyday operations — such as sending notifications, updating records, or generating reports — businesses can streamline workflows and improve productivity.
For instance, a marketing team might manage lead tracking between a website form and their CRM system, while HR could coordinate employee onboarding steps across multiple applications.
Through built-in tools and real-time data synchronization, these platforms eliminate repetitive tasks and help organizations focus on strategic initiatives rather than administrative work.
- Enhanced Flexibility and Integration Across Systems
Modern organizations rely on dozens of applications for analytics, communication, and management. A low-code integration platform acts as the connective tissue between these tools. Whether it’s syncing project data with Slack or integrating analytics dashboards into a CRM, these platforms ensure consistent, accurate, and up-to-date information flow.
Make and Microsoft Power Automate are great examples of scalable integration tools. However, unlike many commercial platforms, Baserow’s open architecture allows you to tailor integrations without vendor lock-in — offering greater transparency and control.
Real-World Example: How Baserow Powers Low-Code Integrations
Let’s take a practical example from the Baserow Community. One user built an internal automation system that connected Baserow with Slack and Google Sheets. By using APIs and simple visual workflows, they created a dashboard that updated team performance metrics in real time, while sending notifications automatically to a shared Slack channel.
This setup not only saved hours of manual data entry but also improved transparency and team coordination.
Another community example involves a logistics startup using Baserow to manage shipment tracking data. They integrated Baserow with their custom delivery app to sync package updates automatically — streamlining operations without hiring additional developers.
These use cases highlight how Baserow’s user-friendly interface and open-source flexibility make it one of the most efficient tools for teams looking to automate workflows and manage complex data seamlessly.
Top Low-Code Integration Platforms to Explore
The market for low-code integration platforms has expanded rapidly, with solutions tailored for various industries and use cases. While each platform has its strengths, the right choice depends on how well it aligns with your team’s goals, technical expertise, and automation needs. Below are some of the most impactful platforms transforming workflow automation today.
1. Baserow
Baserow stands out as a flexible, open-source platform that merges data management and low-code integration into one unified environment. Unlike many proprietary platforms, Baserow gives teams complete control over their data and infrastructure.
It provides a drag and drop interface, real-time collaboration, and API-first design that allows for seamless integration with other systems. Whether it’s automating customer onboarding, syncing data across marketing and CRM tools, or managing internal dashboards, Baserow enables teams to build custom solutions without writing complex code.
A key differentiator is Baserow’s community-driven ecosystem. In the Baserow Community, users regularly share templates, extensions, and automation ideas — from integrating Baserow with Slack to creating workflows for finance and project tracking. Its open architecture also ensures scalability, allowing both small teams and enterprises to evolve their workflows as needs grow.
%20(1).png)
2. Zapier
Zapier is a pioneer in the low-code integration space, best known for its vast library of pre-built app connections (over 6,000). It’s ideal for small and medium-sized teams looking to automate everyday tasks like syncing spreadsheets, sending notifications, or updating CRMs.
While Zapier excels at simplicity, it can become expensive at scale, and some enterprise-level customization may be limited compared to open-source alternatives.
3. Make
Make offers one of the most visual drag and drop interfaces in the industry, allowing users to create sophisticated automations through detailed workflow maps. It’s powerful for technical users who want deeper control without coding from scratch. The platform supports real-time data transfer between tools, making it ideal for analytics and reporting automation.
4. Microsoft Power Automate
Part of Microsoft’s Power Platform suite, Power Automate provides enterprise-grade automation tightly integrated with Office 365, Dynamics, and Azure services. It’s designed for organizations already invested in Microsoft’s ecosystem and supports role-based access, compliance management, and scalable deployment.
5. Appian
Appian focuses on enterprise-level business process automation and application development. Its AI-powered workflows enable advanced process modeling, predictive insights, and compliance tracking. However, Appian’s learning curve and pricing make it better suited for larger organizations with dedicated IT teams.
6. OutSystems
OutSystems offers a robust environment for application development and integration, allowing developers to extend low-code solutions with traditional code when needed. It’s particularly strong in managing complex workflows and multi-platform deployments (web, mobile, and backend systems).
7. Retool
Retool takes a developer-centric approach, blending low-code speed with custom JavaScript support. It’s excellent for teams that need to build web applications rapidly but still want flexibility for custom logic and data manipulation.
8. Mendix
Mendix provides an all-in-one platform for creating user-friendly business apps that connect to multiple data sources. It caters to both developers and citizen developers, offering tools for automating repetitive tasks and maintaining app lifecycle management.
How Baserow Stands Out Among Low-Code Integration Platforms
While each of these platforms has distinct advantages, Baserow uniquely combines the simplicity of a low-code builder with the transparency and flexibility of open-source software. Here’s how it differentiates itself:
- Open-Source Freedom: Baserow allows teams to self-host, modify, and extend functionality without vendor lock-in. This makes it especially appealing for organizations seeking control over their data and infrastructure.
- Visual and User-Friendly Design: Its user-friendly database builder lets users structure information through an intuitive, spreadsheet-like interface. Users can then connect Baserow with external systems to automate workflows effortlessly.
- Powerful API and Extensibility: Developers can use Baserow’s REST API to integrate external tools, while non-technical users can rely on the visual interface to configure automations.
- Real-Time Collaboration and Role-Based Access: Teams can collaborate on shared datasets with real-time visibility and custom permissions. This ensures data integrity and security while maintaining flexibility.
- Active Community and Documentation: The Baserow Community actively contributes plugins, templates, and integrations. This growing ecosystem ensures users can always find new ways to extend their workflows.
- Ideal for Both Technical and Non-Technical Users: Whether you’re building internal dashboards, connecting APIs, or managing data pipelines, Baserow is optimized for both developers and non-developers to work collaboratively.
By balancing open-source transparency with commercial-grade reliability, Baserow positions itself as one of the most adaptive and cost-effective low-code integration platforms available today.
You can read more about how low-code technology is transforming app creation in this related article: No-Code Shaping the Future of Applications.
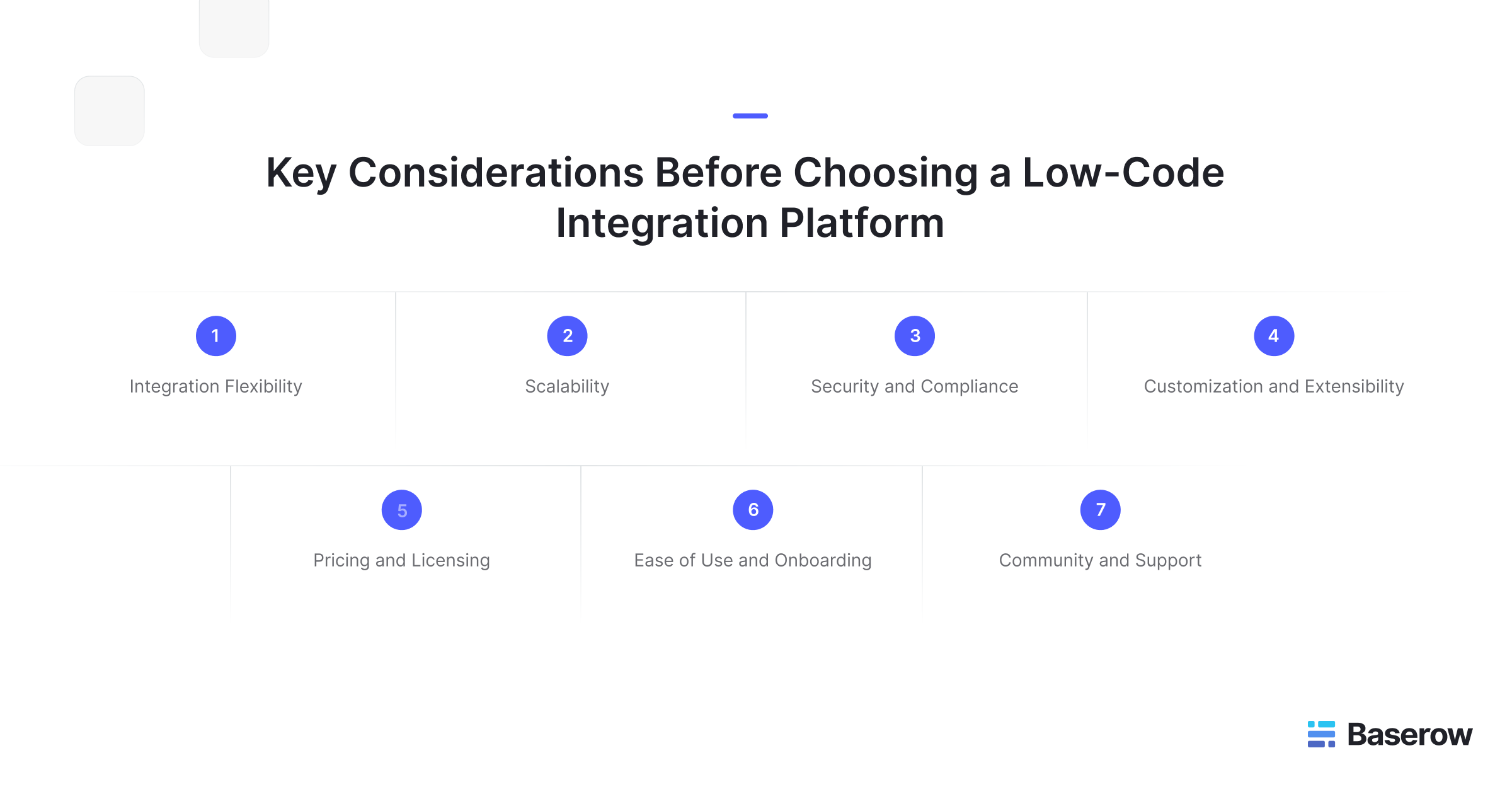
Essential factors to evaluate before making your decision
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the best low-code platform?
The best low-code platform depends on your specific needs — whether you prioritize flexibility, pricing, or ease of integration. For teams seeking open-source freedom and a user-friendly experience, Baserow is one of the most adaptable options. For businesses heavily invested in enterprise software ecosystems, Microsoft Power Automate or Appian may be a better fit.
Ultimately, the best platform is the one that supports your workflows, scales with your business, and empowers both technical and non-technical users.
- What is low-code integration?
Low-code integration refers to connecting different applications or systems using visual interfaces instead of traditional coding. These platforms let users automate data flows, trigger actions between tools, and unify processes through pre-built connectors or APIs. For example, you could link Baserow with Slack to send automatic alerts whenever new data entries are created — all without writing scripts.
- What is a low-code platform?
A low-code platform is a development platform that enables users to create applications or automate workflows using minimal programming. Through drag and drop interfaces, visual models, and automation logic, businesses can design solutions quickly while maintaining control over data and security.
- Who uses low-code platforms?
Low-code tools are used by a broad range of users — from developers who want to accelerate app delivery to business professionals who want to automate workflows independently. Marketing teams, HR departments, operations managers, and analysts all leverage these platforms to streamline business process automation without waiting for IT support.
- What are the 4 types of platforms?
Low-code and no-code tools can generally be categorized into four main types:
- Integration platforms – For connecting and automating systems (e.g., Baserow, Zapier, Make).
- Application development platforms – For building end-to-end apps with visual interfaces (e.g., OutSystems, Mendix).
- Automation platforms – For automating repetitive tasks and process flows (e.g., Power Automate, Appian).
- Database management platforms – For organizing and managing data structures (e.g., Baserow, Airtable).
These categories often overlap, allowing organizations to mix capabilities as needed.
- How to build a low-code platform?
Building a low-code platform from scratch involves combining several elements: a visual interface builder, pre-configured logic blocks, integration APIs, and a secure backend. Platforms like Baserow already provide this foundation, offering open-source access for developers who want to customize or extend functionality. This makes it possible to experiment with your own automation and integration features while learning from an established framework.
- What are low-code examples?
Low-code examples include automating CRM updates, syncing sales data with spreadsheets, or creating internal dashboards that track metrics in real time. For instance, a logistics company might use Baserow to centralize shipment data, while a marketing team uses Zapier to automate email campaigns. These examples show how low-code solutions bridge the gap between people, data, and technology.
Conclusion — Empowering Automation with Low-Code Integration
Low-code integration platforms are redefining how businesses operate. They enable teams to connect systems, automate workflows, and innovate without waiting for traditional development cycles. As organizations continue to scale, the ability to adapt quickly through automation becomes a defining competitive advantage.
Baserow like platforms offer exemplify the new generation of low-code integration tools — flexible, open, and designed for collaboration. With its user interfaces, real-time synchronization, and role-based access, Baserow empowers both developers and non-technical professionals to take ownership of their data and processes.
For startups and enterprises alike, adopting low-code solutions means faster execution, improved agility, and a culture of continuous innovation. Whether you’re looking to automate internal reporting, build connected web applications, or manage complex workflows, Baserow provides the foundation to do it all — without writing extensive code.
If you’re ready to simplify integrations and build smarter workflows, start your journey today.
Baserow 2.1 is a maintenance-focused release that improves performance, security, and reliability. It introduces Expert formula mode, Nuxt 3 and Django upgrades, bug fixes, PostgreSQL 14+ support for self-hosters, and a new Ukrainian translation.

Discover how Airtable and Baserow compare in features, flexibility, speed, and scalability. Compare pricing plans and hidden costs to make an informed decision!

Explore the best open-source software alternatives to proprietary products. Discover OSS tools, licenses, and use cases with our updated directory.
