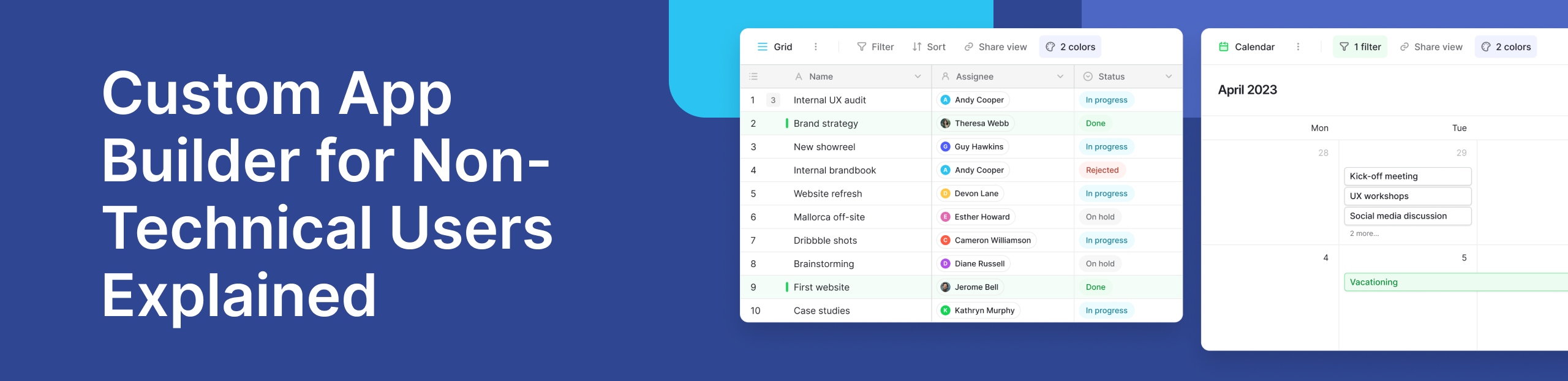
Teams today need software that adapts as fast as their work does. Yet most business users are blocked by one thing: traditional app development assumes you can code. That gap has created strong demand for a custom app builder for non technical users—tools designed to help teams build real applications without engineering skills.
As organisations scale, spreadsheets and ad-hoc tools stop being enough. Teams need structured systems, better collaboration, and reliable access to data in real time. This is where modern no-code platforms step in, making app development accessible without lowering quality or control.
Why Non-Technical Teams Need Custom App Builders
Business teams build workflows every day. They manage requests, track approvals, monitor customers, and coordinate operations. Most of this work starts in Google Sheets, then breaks once processes grow more complex.
Spreadsheets struggle with permissions, automation, and structured relationships. They were never meant to support long-term applications or shared workflows. As a result, teams lose productivity, duplicate work, and rely heavily on developers for even small changes.
A custom app builder removes that dependency. Instead of waiting weeks for changes, teams can create productivity apps themselves, adjust logic instantly, and respond faster to business needs.
What Is a Custom App Builder for Non-Technical Users?
A custom app builder for non technical users is a platform that allows people without programming experience to design, build, and manage applications visually. These tools replace manual coding with configuration and logic blocks.
Unlike pre built solutions that force teams into fixed workflows, these platforms allow full customization. Users define their own data structures, screens, and actions without writing a single line of code.
Most modern builders focus on ease of use while still supporting complex workflows, making them suitable for everything from internal tools to customer-facing systems.
How These Platforms Actually Work
At the core, no-code tools replace programming syntax with visual building blocks. Users interact with a graphical user interface where logic, data, and layout are configured directly.
Features like drag and drop design let users arrange screens and forms intuitively. Data models are created visually, relationships are defined without SQL, and workflows are connected through rules instead of scripts.
Some platforms now include ai powered code tools that assist users by suggesting logic or helping generate workflows automatically. This approach lowers friction while keeping users in control of outcomes.
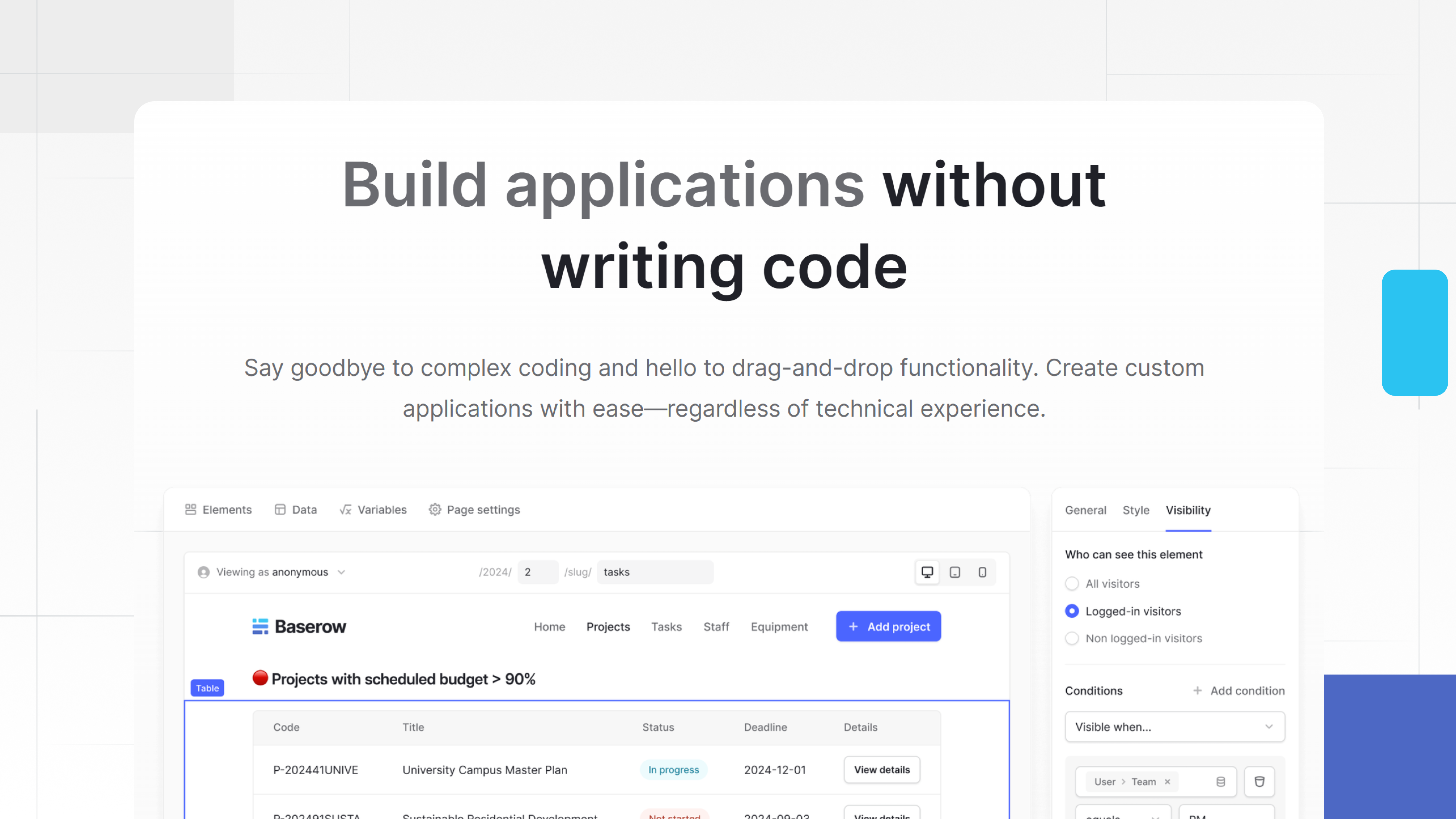
Key Features to Look for in a No-Code App Builder
Not all no-code tools are equal. When evaluating platforms, teams should look for capabilities that support real business use, not just prototypes.
Key features include:
- Support for custom app creation beyond templates
- Visual logic builders that reduce development time
- Secure handling of security data and permissions
- Responsive layouts and clean user interface design
- Built-in automation and ai to generate repetitive logic
- Reliable performance with updates in real time
Enterprise teams should also ensure the platform can scale, support audits, and integrate into existing systems without workarounds.
Where Traditional Coding Platforms Fall Short
Classic coding platforms are powerful but inaccessible. They assume users can write code, manage deployments, and maintain applications long term. For non-technical teams, this creates a permanent bottleneck.
Even small changes often require engineering input. That increases costs and slows iteration. Over time, business teams lose ownership of tools they rely on daily.
Custom app builders flip this model. They let subject-matter experts build and maintain tools themselves, while developers focus on high-impact engineering tasks.
Real-World Use Case: Building Internal Tools with Baserow
A common use case is internal operations management. Teams need custom dashboards, approval flows, and shared data views that evolve frequently.
Using Baserow’s application builder, non-technical users can create internal tools that connect structured data with dynamic interfaces. Instead of relying on static spreadsheets, teams build apps that reflect how work actually happens.
For example, operations teams can create customer portals that surface real-time records, apply permissions, and automate updates without writing scripts. Recent enhancements highlighted in the Baserow 2.0 release notes improve performance, permissions, and application flexibility, making these tools more robust as teams grow.
Baserow’s documentation and application builder overview make onboarding straightforward, while community discussions show how teams apply the platform across operations, product, and support.
Why Baserow Fits Non-Technical Teams Especially Well
Baserow balances simplicity with power. It gives non-developers control without sacrificing structure or governance. Teams can iterate quickly, collaborate safely, and adapt applications as needs change.
Its focus on visual development, combined with optional AI agents to assist logic creation, reduces friction while keeping humans in charge of decisions. That balance is critical for sustainable app development across teams.
AI, Automation, and the Future of No-Code App Development
AI is reshaping how applications are built. Instead of replacing users, AI helps them move faster. Features that suggest workflows or help write code snippets reduce setup time and errors.
The future of no-code lies in collaboration between humans and AI, where automation handles repetition and people handle judgment. Platforms that support this balance will define the next generation of business software.
Common Mistakes Teams Make When Choosing an App Builder
One common mistake is assuming all no-code tools scale the same way. Many platforms are designed for simple demos, not long-term operations or offer enterprise grade. Teams often outgrow them once workflows involve multiple users, permissions, or automation.
Another issue is underestimating security needs. Applications handling internal or customer data must support access control, auditability, and structured ownership. Without this, teams revert back to manual workarounds.
Finally, some teams focus only on speed and ignore maintainability. A good builder should reduce development time without creating long-term complexity. This is where platforms with structured data models and governance features stand out.
How Baserow Supports Scalable, Secure App Development
Baserow is designed to bridge the gap between flexibility and control. Its application builder allows teams to create interfaces directly on top of structured data, instead of copying data into separate tools.
Non-technical users can build internal tools, dashboards, and customer portals while maintaining clear permissions and consistent data. Features introduced in recent updates improve performance, interface flexibility, and collaboration, making the platform suitable for growing teams.
Baserow also integrates well into existing workflows, allowing teams to evolve their tools gradually rather than replacing everything at once. Real examples shared in the Baserow community show teams using the platform for operations tracking, product workflows, and internal request systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can non-technical users really build apps without coding?
Yes. Modern builders use visual logic, drag-and-drop interfaces, and configuration instead of programming, making app creation accessible to non-developers.
- Are no-code apps secure enough for business use?
They can be, if the platform supports permissions, data controls, and structured access. Security depends more on the tool than the approach.
- How long does it take to build a custom app?
Simple tools can be built in hours or days. More complex apps may take longer but still far less time than traditional development.
- Do these apps update in real time?
Most modern platforms support real-time updates so users always see the latest data without manual refreshes.
- What’s the difference between no-code and low-code platforms?
No-code tools require no programming at all, while low-code platforms still expect some coding knowledge for advanced customization.
Getting Started with a Custom App Builder
Choosing the right custom app builder for non technical users starts with understanding your workflows, data needs, and growth plans. The best platforms allow teams to start small, iterate quickly, and scale without rework.
If you’re exploring how to build internal tools or customer-facing applications without increasing engineering load, Baserow provides a practical foundation. Its application builder, documentation, and active community make it easy for teams to experiment and grow confidently.
You can explore the platform and start building your first app by signing up.
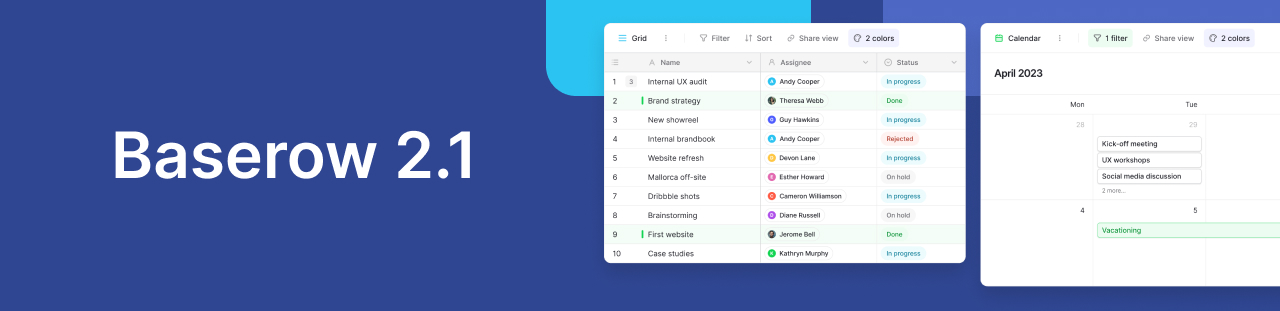
Baserow 2.1 is a maintenance-focused release that improves performance, security, and reliability. It introduces Expert formula mode, Nuxt 3 and Django upgrades, bug fixes, PostgreSQL 14+ support for self-hosters, and a new Ukrainian translation.

Discover how Airtable and Baserow compare in features, flexibility, speed, and scalability. Compare pricing plans and hidden costs to make an informed decision!

Explore the best open-source software alternatives to proprietary products. Discover OSS tools, licenses, and use cases with our updated directory.
