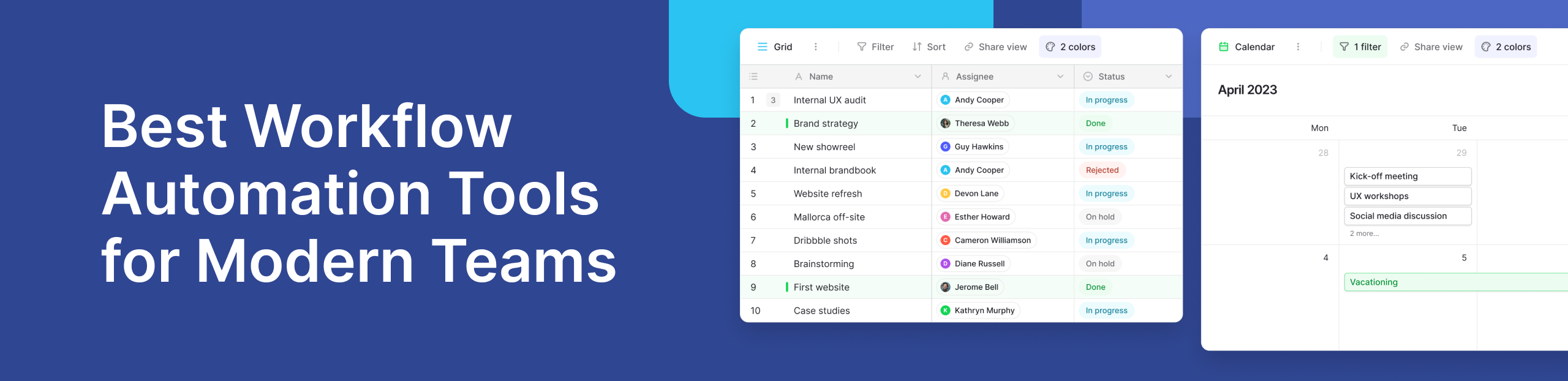
Introduction: Why Workflow Automation Tools Matter Today
As organisations grow and move more of their work online, the need for workflow automation tools rises fast. Teams now deal with tasks spread across many platforms. Customers expect quick responses, and competition keeps increasing. Because of this, automation is no longer optional. It is a key part of how modern teams work.
Today, most teams cannot rely on manual data entry, siloed apps, or scattered spreadsheets. These older methods slow down work, create errors, and make it hard to scale. To stay competitive, companies need tools that reduce manual effort, improve business processes, and automate repetitive tasks in every department.
New automation platforms make this possible. They help teams manage social media posting, customer support, reporting, and internal requests without writing code. With the rise of AI-powered tools, companies can now build smarter workflows that react to changing conditions, spot patterns, and catch issues before they grow.
In this expanding landscape, many teams choose flexible, no-code tools like Baserow. Baserow brings structured data and automation together in one place. Its intuitive interface and modular design help organisations move away from scattered tools and toward a single, scalable workflow system. Many teams start their automation journey by reviewing the Baserow product overview, which shows how centralised data makes workflows clearer, faster, and more reliable.
What Are Workflow Automation Tools?
Workflow automation tools help teams manage their work with fewer manual steps. These platforms run actions that people would normally handle themselves. Most tools let users build processes with drag and drop interfaces, so even non-technical teams can set them up. With a user friendly interface, they make it easy to trigger tasks, assign work, check progress, and complete steps.
These platforms run on simple building blocks. They use triggers, rules, and actions to carry out tasks automatically. The actions can connect to third party apps, send alerts, move data, update records, or create reports. Many tools now add AI agent features that help with more complex decisions.
Industry groups like McKinsey and Gartner note that workflow automation boosts output, cuts costs, and improves accuracy. Because of this, organisations of all sizes now rely on automation for important daily work.
More teams are also choosing open, API-first tools because they allow flexible and custom workflows. Baserow supports this trend with strong integrations and an easy automation engine. The workflow automation guide explains how it works. This setup helps companies build processes that match their exact needs while keeping workflows simple to maintain.
How Workflow Automation Works in Practice
Workflow automation follows a simple cycle. A trigger starts the process. This might happen when someone submits a form, creates a record, or reaches a set date. After the trigger fires, conditions check the details of the event. They decide if the workflow should continue. When the conditions are met, the system runs the next steps. These actions can update data, notify team members, create tasks, or sync with other tools.
AI-powered workflows add more intelligence to this cycle. They look at patterns and make choices based on what they find. They can enrich customer records, sort incoming requests, or tailor messages. These tasks happen without extra manual work.
Baserow’s automation engine uses this same approach. It lets teams build automated flows directly in their database. The automations guide explains how to set up triggers and actions for many types of processes. When teams need something more advanced, Baserow connects with tools like n8n. This allows multi-step flows, complex logic, and data changes across systems.
For a clear walkthrough, you can watch the introductory automation video. It shows how structured data makes each workflow run smoothly and with fewer errors.
.png)
Key Features to Look for in Workflow Automation Tools
Choosing the right automation platform requires understanding the features that will have the biggest operational impact. Among the most important capabilities are:
1. Real-time visibility
Teams need immediate insight into what is working, what is delayed, and where tasks are stuck. Automation tools with real time dashboards or audit trails help ensure accountability across departments.
2. Integrations with a wide range of applications
Work rarely happens in isolation. Platforms that support integrating with third party systems allow data to move smoothly across marketing, finance, operations, engineering, and customer support workflows.
Baserow’s integration ecosystem is built for this purpose. Its integrations page showcases how it connects with external tools, and its partnership with automation platforms like n8n makes it easy to extend even the most customised workflow.
3. Flexible workflow builders
The ability to design processes using drag and drop interfaces makes automation far more accessible. It empowers non-technical teams to create, test, and optimise workflows without relying on developers.
4. User-friendly interface and low learning curve
If an automation tool is too complex, adoption fails. The best platforms provide clarity, clean UI, and guided onboarding so users can build workflows confidently.
5. Strong customer support
With more processes automated, teams depend heavily on their automation platform. Tools that offer responsive support reduce downtime and risk.
Teams that want a deeper look at how automation improves operational performance can explore Baserow’s broader approach to business process optimisation in the business automation software resource. It highlights how structured data, clear workflows, and flexible automation features come together to reduce friction and strengthen day-to-day operations.
Comparing Workflow Automation Tools: What Teams Actually Need
As the automation landscape grows, teams often struggle to evaluate which platform matches their operational needs. Some tools specialise in simple task routing, while others offer highly customisable environments with deep integrations, real-time processing, and AI-driven capability. The challenge is not finding automation tools—there are many—it is identifying the one that aligns with your workflow complexity and team structure.
For a project manager, workflow automation means faster task handovers, predictable scheduling, and clearer resource allocation. For customer support teams, automation helps classify tickets, escalate urgent cases, and ensure that responses remain consistent. Marketing teams lean on automation for social media posting, content approvals, and lead nurturing, while operations teams depend heavily on accurate data flows to avoid bottlenecks across business processes.
Each department has different needs, but the underlying requirement is the same: a system that automates repetitive tasks while remaining flexible enough to evolve. Tools that lock teams into rigid sequences or that lack modularity ultimately become barriers rather than enablers.
Many organisations turn to flexible database-driven tools because they allow workflows to adapt as the business grows. This is one area where platforms like Baserow stand out. Because Baserow is built as a scalable, structured data layer, teams can automate any process tied to their database — from content approvals to request intake to internal logistics. This makes it different from single-purpose tools that cannot grow with evolving operational needs. Baserow’s product overview offers a clear understanding of how databases, views, and automations connect to form an integrated workflow environment.
Why Baserow Is One of the Most Versatile Workflow Automation Tools
Baserow offers an edge over many traditional automation platforms. It combines a no-code database with a full automation engine in one place. This lets teams keep their data, processes, and integrations together. It also removes the fragmentation that happens when companies use different tools for storage, workflow design, and integrations.
Baserow’s automations page explains how teams can build workflows that run when events occur. These events might include new entries, updates, time-based triggers, or inputs from other systems. The actions can update data, send notifications, or trigger more steps — all without code.
Many organisations also want automation tools that are easy to try. Free plans are helpful here, as teams can explore automation without long-term commitments. Baserow supports this with a simple way to start building structured processes at no cost, while still giving teams room to grow into advanced workflows later.
For cross-platform workflows, Baserow’s integrations add even more flexibility. The integrations page shows how it connects to many external apps, from CRMs to marketing and messaging tools. For complex automation, Baserow works well with n8n, a popular orchestrator. The n8n Baserow integration shows how to build multi-step flows, use deeper logic, or sync large sets of data.
To help new users, Baserow also offers a guided video tutorial. It walks through each step of building automations. This is especially useful for teams moving from spreadsheets to more dynamic workflow systems.
Strengthened by Baserow 2.0
Recent advancements in the Baserow 2.0 release introduced improved performance, faster data processing, and enhanced user interface updates. These upgrades make workflows run smoother, reduce latency in real-time updates, and provide a cleaner automation builder experience. As organisations scale, these improvements ensure that workflow reliability and system responsiveness are maintained.
What the Community Is Doing With Automations
The Baserow community frequently shares use cases that highlight how adaptable the platform is. In community discussions, users have automated everything from order management flows and team scheduling to editorial calendars and customer onboarding sequences. These scenarios showcase how the combination of structured data and automation logic enables powerful outcomes, even for teams without technical expertise.
One member recently explained how they automated a complete internal request system—routing requests to different teams, notifying stakeholders, updating statuses, and summarising activity daily—without writing a single line of code. These types of examples illustrate how flexible automation empowers teams to focus more on decision-making and less on repetitive admin tasks.
How a Scaling Team Automated Operations With Baserow
Sharing a quick use case. Consider a fast-growing service-based organisation handling thousands of incoming requests weekly. Before automation, the team relied on email inboxes, spreadsheets, and manual tracking. Tasks were often duplicated, misplaced, or delayed due to unclear ownership.
After switching to Baserow, the team created a structured intake database to centralise all incoming requests. From there:
- An automation would route each submission to the correct department based on predefined rules.
- Customer support could prioritise tickets automatically using categorisation logic.
- Managers received real-time dashboards with pending, escalated, and completed tasks.
- Integrated flows with third-party tools synchronised updates across communication platforms.
The result was a 40–60% reduction in manual workload, significantly faster processing times, and complete visibility into performance metrics. By eliminating manual data handoffs and enabling real-time coordination, the organisation scaled its support operations without hiring additional staff.
This example demonstrates how workflow systems backed by structured data—such as those built in Baserow—create long-term operational resilience.
How Workflow Automation Tools Work Behind the Scenes
A complete workflow consists of three basic elements:
- Triggers – the event that starts a workflow.
• Actions – the automated tasks performed.
• Conditions – logic determining when actions should run.
Most automation tools rely on this pattern, but AI-powered systems enhance it further. They use AI agent–driven predictions and contextual understanding to decide which action path is appropriate—helping teams classify requests, enrich customer data, or pre-fill information with minimal human involvement.
For businesses using Baserow, this logic is captured in the automation builder documented in the workflow automation user guide. The system shows how triggers and actions map to real tasks, making it simple for non-technical teams to orchestrate even multi-step processes. Those who need advanced orchestration can pair Baserow with n8n, allowing cross-tool interactions and multi-layer logic that supports sophisticated, enterprise-grade workflows.
5 Steps of Building an Effective Workflow
.png)
Teams exploring workflow automation often ask what the foundational steps of workflow design are. Whether the process is simple or deeply structured, nearly every workflow follows these five core steps:
1. Define the objective
Workflows begin by identifying the problem they solve—such as reducing manual effort, routing information faster, or creating consistent approval processes.
2. Map the process
This stage outlines tasks, decision points, owners, and expected outcomes. Many teams use digital whiteboards or process diagrams to establish clarity.
3. Assign responsibilities
Understanding who performs what action—often mapped using L1, L2, L3, and L4 processes—ensures accountability. These levels represent the stages of operational maturity, from entry-level tasks (L1) to highly strategic oversight (L4).
4. Automate and configure
This is where workflow automation tools come in. Teams select triggers, conditions, and actions to automate repetitive tasks. In platforms like Baserow, the automation configuration is handled via an intuitive, no-code builder that lets users set up flows directly from their structured data.
5. Test, monitor, and optimise
Workflows evolve. Testing ensures accuracy, and monitoring reveals bottlenecks. Real time updates help teams refine steps as needs change.
When these five steps are executed clearly, organisations gain better visibility, smoother collaboration, and scalable processes that withstand growth.
Types of Workflows (and When to Use Them)
Teams often ask what the four types of workflows are. In practice, they fall into these categories:
1. Sequential workflows
Each task must be completed before the next begins—often used for approvals or onboarding.
2. State machine workflows
Processes move between different states based on conditions, ideal for ticketing or customer support.
3. Rule-based workflows
Logic-driven flows used to classify leads, prioritise tasks, or route information based on criteria.
4. Event-driven workflows
Triggered by real-time conditions, such as form submissions, approaching deadlines, or new data entries.
Workflow automation tools need to support all four types, especially for teams coordinating high-volume operations. Baserow enables these patterns through structured data views, conditional logic, and event-based triggers.
Three Phases of Workflow (The High-Level View)
From a strategic perspective, every workflow moves through three overarching phases:
Phase 1: Input
Information is gathered—through forms, submissions, or integrated systems.
Phase 2: Processing
Logic and actions transform the input into outcomes.
Phase 3: Output
Results are delivered—notifications, updates, completed tasks, or reports.
The clarity of these phases helps explain why database-backed automation platforms like Baserow work well. Because structured data is centralised, workflows can be built directly around the input, processing, and output layers in one place.
Limitations of Automation (And How to Overcome Them)
Even the best workflow automation tools have limitations:
1. Over-automation risks
If teams automate every edge case, workflows become too rigid. To avoid this, automations should focus on predictable, repeatable actions while leaving contextual decisions to humans.
2. Data dependency
Poor data quality leads to poor workflow outcomes. Tools like Baserow help mitigate this by enforcing structure and reducing manual data entry that introduces errors.
3. Lack of visibility
Some automation platforms do not provide clear logs. Visibility is essential for diagnosing failures. Baserow’s real-time updates and consistent interface provide insights into workflow execution.
4. Integration gaps
Tools that cannot integrate with third party systems limit the automation’s potential. Baserow addresses this through its integrations ecosystem as well as partnerships with tools like n8n.
Understanding these limitations helps teams implement smarter, safer workflows that improve reliability rather than create operational risks.
The Future of Workflow Automation Tools
Automation is entering a new era driven by intelligent systems. AI agent–powered workflows will increasingly:
- Predict the next best action
- Assist with decision-making
- Enhance real-time processing
- Reduce dependency on manual oversight
Meanwhile, organisations are shifting toward platforms that combine databases, automation, and integrations under a unified environment. This is why tools like Baserow gain traction—they enable teams to manage data, create automations, integrate systems, and visualise processes all in one place. This holistic approach supports long-term scaling without forcing migrations to new systems.
Modern workflow automation also leans heavily on transparency, operational flexibility, and user autonomy. As Baserow continues to evolve—particularly with improvements highlighted in the Baserow 2.0 release notes—teams can expect faster processing, more automation features, and greater support for complex workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the 5 steps of workflow?
Define the objective, map the process, assign responsibilities, automate, and optimise.
- How does workflow automation work?
It uses triggers, conditions, and actions to perform tasks automatically based on predefined logic.
- What are the four types of workflows?
Sequential, state machine, rule-based, and event-driven workflows.
- What are the three basic elements of a workflow?
Triggers, actions, and conditions.
- What are the limitations of automation?
Over-automation, poor data quality, integration gaps, and lack of transparency.
- What are the three phases of workflow?
Input, processing, and output.
- What are the 4 stages of process automation?
Assessment, design, implementation, and optimisation.
- What are the three basic workflow activities?
Creation, transformation, and completion.
- What are L1, L2, L3, and L4 processes?
Levels of operational maturity and responsibility, ranging from basic task execution to strategic oversight.
Final Thoughts
Workflow automation tools have become a core part of how modern organisations operate. Whether improving internal communication, streamlining decision-making, or reducing manual workload, automation helps teams work faster and smarter. With flexible platforms like Baserow—complete with structured data, automations, integrations, and continuous improvements—businesses can build workflows tailored to their exact needs while maintaining scalability and performance.
Teams ready to begin should explore Baserow’s capabilities and begin building their own automated workflows.
Start your journey here: Create your free Baserow account.
Baserow 2.1 is a maintenance-focused release that improves performance, security, and reliability. It introduces Expert formula mode, Nuxt 3 and Django upgrades, bug fixes, PostgreSQL 14+ support for self-hosters, and a new Ukrainian translation.

Discover how Airtable and Baserow compare in features, flexibility, speed, and scalability. Compare pricing plans and hidden costs to make an informed decision!

Explore the best open-source software alternatives to proprietary products. Discover OSS tools, licenses, and use cases with our updated directory.
