Assign roles to teams at workspace level
Assigning roles to teams at the workspace level lets workspace admins control permissions for entire groups in one action, with automatic inheritance throughout databases and tables.
This guide covers how to assign and modify roles for teams at the workspace level, understand role hierarchy and inheritance, and implement advanced permission strategies for bulk access control.
Paid feature: Role-based permissions are available on the Baserow Advanced and Enterprise plans. View pricing details.
Overview
When you assign a default role to a team at the workspace level, every team member automatically receives that role across the entire workspace and all its contents, unless you set specific exceptions at the database or table level. This bulk permission management is more efficient than assigning roles individually, especially for organizations with structured departments or project groups.
Team roles work alongside individual member roles. When conflicts occur, individual permissions always take precedence over team permissions. This allows you to set broad team defaults while making targeted exceptions for specific members.
Learn more: Role assignment hierarchy
When to use workspace-level team roles
| Use Case | Why it works |
|---|---|
| Department-wide access | Give entire departments consistent permissions across all workspace content |
| Client teams | Assign external client teams Viewer or Commenter access to specific project data |
| Project groups | Create temporary teams for projects with unified access needs |
| Role-based groups | Organize by function (Editors, Reviewers, Analysts) rather than organizational structure |
When you remove a member from a team, they immediately lose all team-based permissions but retain any individual permissions assigned directly to them.
Learn more about managing team membership.
Assign or modify team roles
Prerequisites: Before assigning roles to teams, you must first invite users to your workspace and create a team.
View current team roles
- Open your workspace from the dashboard
- Select Members in the sidebar or workspace menu options
- Click the Teams tab to view all workspace teams
The Teams tab displays each team’s current default role at the workspace level.
Change a team’s default role
- On the Teams tab, locate the team you want to modify
- Click the default role dropdown next to the team name
- Select the new role from the list:
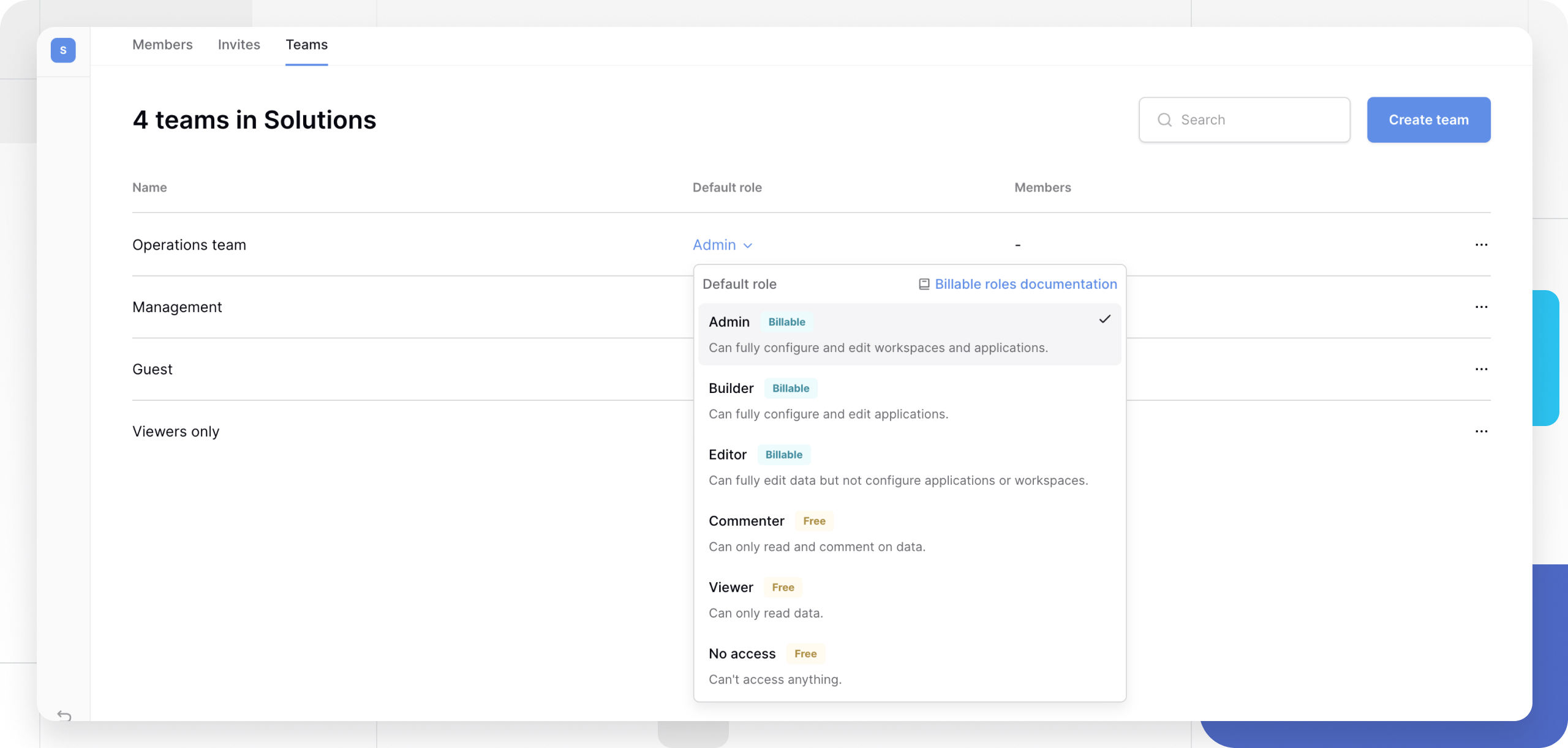
The role change applies immediately to all team members across the workspace, unless they have individual permission overrides.
Advanced permission strategies
Teams can be organized hierarchically by assigning roles to teams at the workspace level.
Strategy 1: “No Role” baseline with targeted access
Individual permissions always take precedence over team permissions. For maximum control over permissions, use this recommended approach:
- Assign individual members “No Role” at workspace level
- Create teams and add members to appropriate teams
- Assign team roles at database and table levels only (not workspace level)
The workspace members have no default access. They only get permissions through their team memberships at specific database/table levels. This prevents accidental access and creates a “least privilege” security model.
Learn more about role hierarchy.
Example implementation:
All individual members: No Role at workspace level
├── Finance Team: No role at workspace → Admin on Finance database
├── Marketing Team: No role at workspace → Editor on Campaigns database
└── External Reviewers: No role at workspace → Viewer on Reports database
Strategy 2: Team hierarchies
Create nested permission structures where higher teams can access everything lower teams own. Assign broader roles (e.g., Editor) to leadership teams, assign narrower roles to operational teams, and then higher-level teams can inherit access to lower-level content.
Learn more about role hierarchy.
Strategy 3: Exception-based permissions
Set generous workspace-level team roles, then restrict access where needed:
- Assign the team a broad role (e.g., Editor) at the workspace level
- Set database-level exceptions for sensitive content (database permissions)
- Set table-level exceptions for specific restrictions (table permissions)
Example:
- Sales Team: Editor at workspace level
- Exception: Commenter on Commission Database
- Exception: Viewer on Management Reports Table
Frequently asked questions
Do workspace-level team roles apply to new databases and tables?
Yes. When you create new databases or tables, team members automatically have their workspace-level team role on the new content, unless you set specific exceptions.
Can I see the permission a team member has?
Yes. On the Members page, users with the right access can view the default role and highest role an individual member has across all databases and tables.
What happens if I change a team’s role after setting database exceptions?
Database and table-level exceptions remain in place. Changing the workspace-level team role only affects areas where no exceptions exist.
Should I use teams or individual permissions?
Use teams when multiple members need the same permissions. Use individual permissions when specific members need unique access that differs from their team. Combining both provides maximum flexibility.
How do I audit team permissions across my workspace?
Navigate to the Members page to view all teams and their roles. For detailed permission tracking, audit logs record all permission changes. Learn more about audit logs.
Can a member belong to multiple teams with different roles?
Yes. When a member belongs to multiple teams, they receive the highest permission level from any team they’re part of. Individual permissions still override all team permissions.
Related content
- Create and manage teams
- Understand role hierarchy
- Role levels in Baserow
- Assign roles to members at workspace level
- Assign roles at database level
- Assign roles at table level
- Permissions overview
Still need help? If you’re looking for something else, please feel free to make recommendations or ask us questions; we’re ready to assist you.
-
Contact support for questions about Baserow or help with your account
- On this page
- Overview
- When to use workspace-level team roles
- Assign or modify team roles
- Advanced permission strategies
- Frequently asked questions
- Do workspace-level team roles apply to new databases and tables?
- Can I see the permission a team member has?
- What happens if I change a team’s role after setting database exceptions?
- Should I use teams or individual permissions?
- How do I audit team permissions across my workspace?
- Can a member belong to multiple teams with different roles?
- Related content