Database API documentation
Baserow’s API-first approach makes it easy to integrate databases with any application, automate workflows, and build custom solutions without vendor lock-in.
Baserow provides REST APIs for all database operations using token-based authentication. Access auto-generated docs through your database settings, authenticate with tokens, and use standard HTTP methods for CRUD operations on tables and rows.
Overview
Baserow automatically generates REST API documentation for every database you create. The API follows REST conventions, uses JSON for data exchange, and provides standard HTTP status codes for clear error handling.
Authentication uses database tokens with granular permissions down to the table level. You can control create, read, update, and delete access per token, ensuring secure integration with external applications.
The API documentation updates automatically when you modify your database schema, keeping your integration code in sync with your data structure changes.
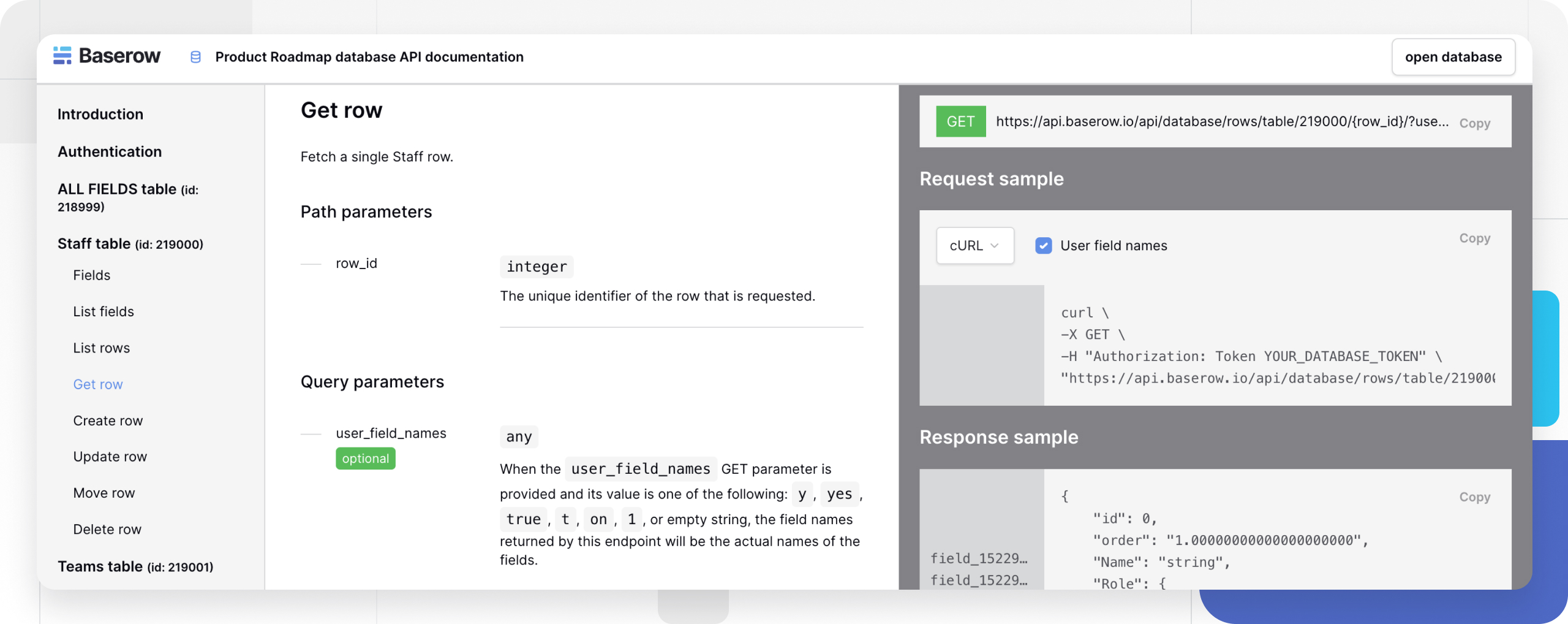
Access database API documentation
- Click the vertical ellipsis
⋮next to your database name - Select View API Docs from the menu
- Review auto-generated endpoints specific to your schema
- Make your first API call
curl \
-X GET \
-H "Authorization: Token YOUR_DATABASE_TOKEN" \
"https://api.baserow.io/api/database/fields/table/TABLE_ID/"
Learn how to generate a database token for a workspace.
Core API endpoints
Test endpoints with tools like curl or Postman.
| Operation | Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| List tables | GET |
/api/database/tables/all-tables/ |
Get all tables in workspace |
| List fields | GET |
/api/database/fields/table/{table_id}/ |
Get field schema for table |
| List rows | GET |
/api/database/rows/table/{table_id}/ |
Get all rows with filtering/pagination |
| Get row | GET |
/api/database/rows/table/{table_id}/{row_id}/ |
Get specific row by ID |
| Create row | POST |
/api/database/rows/table/{table_id}/ |
Add new row to table |
| Update row | PATCH |
/api/database/rows/table/{table_id}/{row_id}/ |
Modify existing row |
| Move row | PATCH |
/api/database/rows/table/{table_id}/{row_id}/move/ |
Change row position |
| Delete row | DELETE |
/api/database/rows/table/{table_id}/{row_id}/ |
Remove row from table |
Anatomy of a Baserow API Endpoint
https://api.baserow.io/api/database/rows/table/TABLE_ID/?user_field_names=true
| Component | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Base URL | Baserow API server | https://api.baserow.io (Cloud)https://your-domain.com (Self-Hosted) |
| API Path | Endpoint structure | /api/database/rows/table/ |
| TABLE_ID | Unique identifier for your table | 12345 |
| Parameters | Query string options | ?user_field_names=true |
Authentication
Baserow uses token authentication for API access. Tokens are scoped to specific databases and tables. Permissions can be set to create, read, update, delete per table. Use specific table permissions rather than full database access.
All API requests must use HTTPS and must include the database token in the Authorization header.
Authorization: Token YOUR_DATABASE_TOKEN
Tokens can be revoked at any time from the account settings.
Store tokens securely and rotate regularly (environment variables, not in code).
Rate limits
Monitor rate limits, API usage and performance on cloud instances.
Cloud version: In Baserow Cloud, there’s a limit of 10 concurrent API requests. This limit is subject to a fair use policy, and we reserve the right to lower it if it affects overall performance. Self-hosted: No rate limits
Working with field types
Different field types require specific data formats when creating or updating rows.
Text and numeric fields
{
"Name": "John Doe",
"Age": 25,
"Email": "john@example.com"
}
Select fields
Provide either the option names or internal IDs:
Single select:
Accepts an integer or a text value representing the chosen select option ID or option value. A null value means none is selected. In case of a text value, the first matching option is selected.
{
"Timezone": {
"id": 1,
"value": "Option",
"color": "light-blue"
}
}
Multiple select:
Accepts an array of mixed integers or text values, each representing the chosen select option ID or value. In case of a text value, the first matching option is selected. You can send a string with names separated by a comma as a value, in which case the string is converted into an array of option names.
{
"Team": [
{
"id": 1,
"value": "Option",
"color": "light-blue"
}
]
}
Link to table fields
Accepts an array containing the identifiers or main field text values of the related rows from the table ID. All identifiers must be provided every time the relations are updated. If an empty array is provided, all relations will be deleted. In case of a text value instead of an identifier, a row with the matching value for its main field will be searched. If more than one match is found, the first one in the order of the table is selected. You can send a string with names separated by a comma, in which case the string is converted into an array of row names. You can also send only the ID of a row alone.
Reference related rows by primary field value or ID:
{
"Customer": [
{
"id": 0,
"value": "string"
}
]
}
Date and boolean fields
{
"Created": "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z",
"IsActive": true
}
Error handling
Baserow uses standard HTTP status codes with detailed error messages. Implement proper error handling and retry logic in your application.
Common status codes:
| Error code | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | Ok | Request completed successfully. |
| 400 | Bad request | The request contains invalid values or the JSON could not be parsed. |
| 401 | Unauthorized | When you try to access an endpoint without a valid database token. |
| 404 | Not found | Row or table is not found. |
| 413 | Request Entity Too Large | The request exceeded the maximum allowed payload size. |
| 500 | Internal Server Error | The server encountered an unexpected condition. |
| 502 | Bad gateway | Baserow is restarting or an unexpected outage is in progress. |
| 503 | Service unavailable | The server could not process your request in time. |
Error response format
{
"error": "ERROR_NO_PERMISSION_TO_TABLE",
"description": "The token does not have permissions to the table."
}
Filtering and pagination
Query parameters for listing rows
Filtering:
filters: JSON object with filter conditions. Rows can optionally be filtered using the same view filters that are available for the views.filter_type: “AND” or “OR” for multiple filters. This works only if two or more filters are provided.search: Full-text search across all fields. If provided, only rows with data that matches the search query are going to be returned.
Sorting:
order_by: Field name to sort by. By default or if prepended with a ‘+’, a field is ordered in ascending (A-Z) order, but by prepending the field with a ‘-’, it can be ordered descending (Z-A).
Pagination: Use pagination for large datasets.
size: Number of rows per page (default 100, max 200)page: Page number (starts at 1)
GET /api/database/rows/table/123/?filters={"Status":"Active"}&order_by=-Created&size=50&page=2
OpenAPI specification
The OpenAPI spec includes detailed parameter descriptions, request/response examples, and can be imported into API testing tools like Postman or Insomnia.
Access the complete API specification:
- Interactive docs: https://api.baserow.io/api/redoc/
- JSON schema: https://api.baserow.io/api/schema.json
Webhooks integration
Combine API calls with webhooks for real-time data synchronization.
Webhooks notify your application when data changes. API calls let you query and update data programmatically. Together, they enable bi-directional integration workflows.
Learn more about Baserow webhooks
Frequently asked questions
How do I find my table and database IDs?
Table and database IDs are visible in your browser URL when viewing a table, or you can retrieve them via the list tables endpoint. Learn more about finding IDs.
Can I use the API without creating an account?
No, all API endpoints require authentication with a database token, which requires a Baserow account and access to the relevant database.
What happens when I change my database schema?
The API documentation automatically updates to reflect your schema changes. However, you may need to update your client code if field names, types, or table structures change. Cache table schema information when possible.
How do I handle API rate limits?
Cloud users should implement retry logic with exponential backoff. Self-hosted instances have no rate limits. Monitor response headers for rate limit status.
Can I bulk create or update multiple rows?
The standard API creates/updates one row per request. For bulk operations, make multiple API calls or consider using the batch endpoints if available in your plan.
How do I debug API authentication issues?
Verify your token is correct, has proper permissions for the table, and is included in the Authorization header as Token YOUR_DATABASE_TOKEN. Check that your database and table IDs are accurate.
Related content
- Generate database tokens
- Database and table IDs guide
- Baserow webhooks
- Zapier integration: No-code automation platform
- Make integration: Visual workflow builder
- n8n integration: Open-source workflow automation
Still need help? If you’re looking for something else, please feel free to make recommendations or ask us questions; we’re ready to assist you.
- Ask the Baserow community
- Contact support for questions about Baserow or help with your account.