Snapshots
Snapshots are complete database copies that capture your entire database at a specific moment, enabling you to restore data to that exact state if needed.
This guide covers how to create, restore, and manage Baserow snapshots for point-in-time database backups and disaster recovery.
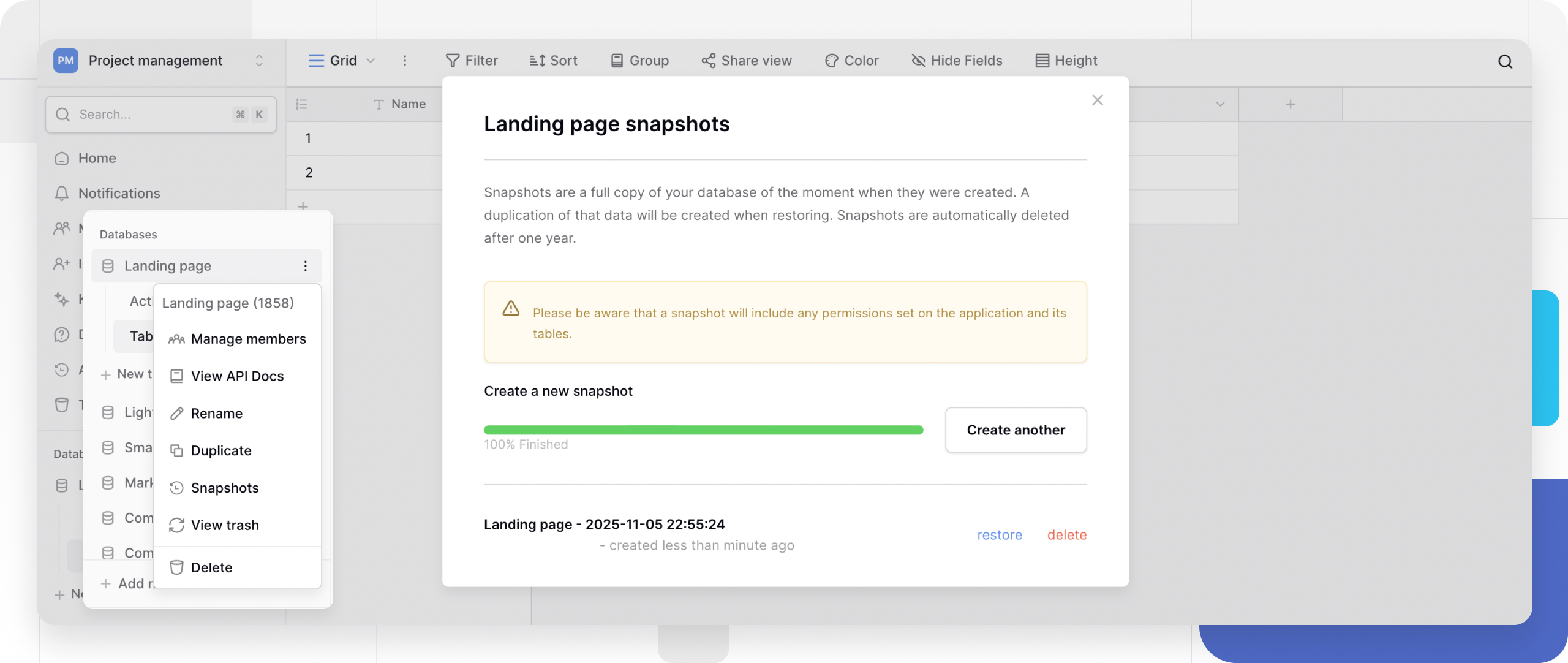
What are snapshots?
Snapshots create full backups of databases that can be restored to recover from data loss or corruption. Unlike trash recovery, snapshots persist until you delete them, providing long-term backup protection for critical databases.
Snapshots include:
- All tables and their data (every row, field, and value)
- All views and view configurations (filters, sorts, field visibility)
- Field types and configurations
- Link to table relationships between tables
- All file attachments and images
Snapshots do NOT include:
- Other databases in the same workspace
- Webhooks configurations
Snapshots vs other backup methods
Different backup methods serve different purposes:
| Method | Retention | Scope | Restore speed | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snapshots | Until deleted | Entire database | Fast | Complete database recovery |
| Trash | 3 days | Individual items | Instant | Accidental deletions |
| Table export | Manual storage | Single table | Slow (re-import) | Sharing data externally |
| Workspace export | Manual storage | All databases | Slow (re-import) | Migration between instances |
| Undo/Redo | Session only | Recent actions | Instant | Immediate mistakes |
How to create a snapshot
Snapshots capture your entire database at the current moment. Create snapshots before major changes or on regular schedules for ongoing protection.
- Navigate to your workspace and locate the database
- Click the three-dot menu (⋮) next to the database name
- Select Snapshots from the dropdown
- Click Create snapshot in the snapshots modal
- Enter a descriptive name for the snapshot (e.g., “Before Q4 migration” or “Pre-formula update 2024-01-15”)
- Click Create
Snapshot creation time: Large databases may take several minutes to snapshot. You’ll see a progress indicator and can continue working in other databases while the snapshot completes.
How to restore a snapshot
- Click the three-dot menu (⋮) next to your database name
- Select Snapshots from the dropdown
- Find the snapshot you want to restore in the list
- Select Restore snapshot
All tables, views, rows, and fields reflect the snapshot moment. Data added after the snapshot is not visible. Files and attachments reflect to snapshot versions
Manage snapshots
View all snapshots
- Click the three-dot menu (⋮) next to your database
- Select Snapshots
- The modal shows all snapshots with the Snapshot name, Creation date and time, and who created the snapshot.
Delete snapshots
Remove outdated or unnecessary snapshots to free up storage and reduce clutter.
- Open the Snapshots modal for your database
- Find the snapshot to delete
- Select Delete snapshot
- Confirm the deletion
Warning: Deleted snapshots cannot be recovered. Ensure you don’t need the snapshot before deleting it. Consider keeping at least one recent snapshot for emergency recovery.
Cancel snapshot creation
For large databases, snapshot creation can take several minutes. Cancel in-progress snapshots if needed.
- Open the Snapshots modal
- Find the in-progress snapshot (shows progress indicator)
- Click Cancel next to the snapshot job
- Confirm cancellation

Canceled snapshots are discarded and don’t count toward storage. The cancellation helps manage system resources when creating snapshots for very large databases.
Snapshot permissions
Who can create snapshots
Only workspace members with Admin roles can create, restore, list, and delete snapshots. Lower permission levels (Builder, Editor, Commenter, Viewer) cannot access snapshot functionality.
Permissions preserved in snapshots
When you create a snapshot, all database and table permissions are captured:
- Workspace member role assignments
- Team-level permissions
- Database-level role assignments
- Table-level role assignments
Why use snapshots?
Snapshots provide backup and recovery that goes beyond basic export/import workflows.
Point-in-time recovery: Restore databases to exact states from specific moments. Critical before major data migrations, bulk updates, or structural changes.
Disaster recovery: Protect against accidental bulk deletions, corrupted imports, or failed integrations. Snapshots let you roll back entire databases when exports would be too slow.
Compliance and auditing: Many industries require point-in-time backup capabilities for compliance. Snapshots provide timestamped, complete database copies for audit trails.
Testing and staging: Create snapshots before testing new workflows, formulas, or integrations. Restore quickly if tests damage data or structures.
Version control for databases: Maintain snapshots at project milestones or release points. Roll back to previous versions if new changes cause issues.
Use snapshots when:
- You need guaranteed recovery points beyond 3 days
- Database recovery speed is critical (faster than re-importing exports)
- Compliance requires point-in-time backups
- You’re making risky bulk changes to production databases
- You need to preserve the exact database state, including permissions
Use exports when:
- You need to share data with external parties
- You’re migrating to different Baserow instances
- You want backups stored outside Baserow
- You’re on Premium or lower plans without snapshot access
When to create snapshots
Before bulk operations:
- Large imports that modify existing data
- Bulk deletions or field removals
- Database structure changes (adding/removing tables)
- Complex formula updates affecting many fields
Regular intervals:
- Daily for critical production databases
- Weekly for regularly updated databases
- Monthly for reference or historical databases
Before major milestones:
- Product releases or launches
- End of quarter/year
- Migration to new systems
- Integration installations
Before testing:
- New workflow implementations
- Third-party integration tests
- Experimental formula or automation changes
Frequently asked questions
How much storage do snapshots use?
Snapshots store complete database copies, so they consume storage equal to the database size at snapshot time. Large databases with many files create large snapshots. Monitor snapshot storage and delete outdated snapshots to manage storage costs.
How long does snapshot creation take?
Creation time depends on the database size. Small databases (under 100 rows) snapshot in seconds. Large databases (10,000+ rows with files) may take several minutes. You can continue working in other databases while snapshots are created in the background.
Can I schedule automatic snapshots?
Not currently through the Baserow UI. For automated snapshots, use the Baserow API with external automation tools or cron jobs.
Can I restore snapshots to different databases or workspaces?
No. Snapshots restore only to the database they were created in. To copy database structure or data to different workspaces, use workspace exports and imports instead.
Do snapshots include deleted items from trash?
No. Snapshots capture the database’s current state, which doesn’t include items in trash. Items deleted before the snapshot was created won’t appear in snapshot restorations.
Can I download snapshots for offline storage?
Not directly. Snapshots are stored within Baserow’s infrastructure. For offline backups, use table exports or workspace exports, which download to your local system. Consider combining both approaches for comprehensive backup strategies.
How many snapshots can I keep per database?
Generally, there’s no hard technical limit, but storage costs and management complexity increase with many snapshots. A common practice is keeping daily snapshots for a week, weekly for a month, and monthly for a year.
How can I restore previous data changes in Baserow?
You can review all row changes in the Audit log available in the left sidebar. This shows which rows were updated and by whom. If you are self-hosting, all data is stored in your PostgreSQL database. If you have a database backup, you can restore it to recover the earlier state. Be aware that restoring a backup will revert all data changes made after the backup was created, not just the affected rows.
Related resources
Backup and recovery
- Delete and recover data - Trash and undo/redo
- Export tables - Download table backups
- Export workspaces - Complete workspace backups
- Import data - Restore exported data
Permissions
- Permissions overview - Role-based access control
- Assign roles at database level - Database permissions
- Create and manage teams - Team-based access
Account management
- Account settings overview - Manage your account
- Password management - Account security
Plans and features
- Pricing plans - Feature availability by plan
Still need help? If you’re looking for something else, please feel free to make recommendations or ask us questions; we’re ready to assist you.
-
Contact support for questions about Baserow or help with your account
- On this page
- What are snapshots?
- Snapshots vs other backup methods
- How to create a snapshot
- How to restore a snapshot
- Manage snapshots
- Snapshot permissions
- Why use snapshots?
- Frequently asked questions
- How much storage do snapshots use?
- How long does snapshot creation take?
- Can I schedule automatic snapshots?
- Can I restore snapshots to different databases or workspaces?
- Do snapshots include deleted items from trash?
- Can I download snapshots for offline storage?
- How many snapshots can I keep per database?
- How can I restore previous data changes in Baserow?
- Related resources