Introduction to tables in Baserow
Tables are where your data lives in Baserow. Baserow tables combine spreadsheet familiarity with database power; organize once, visualize many ways.
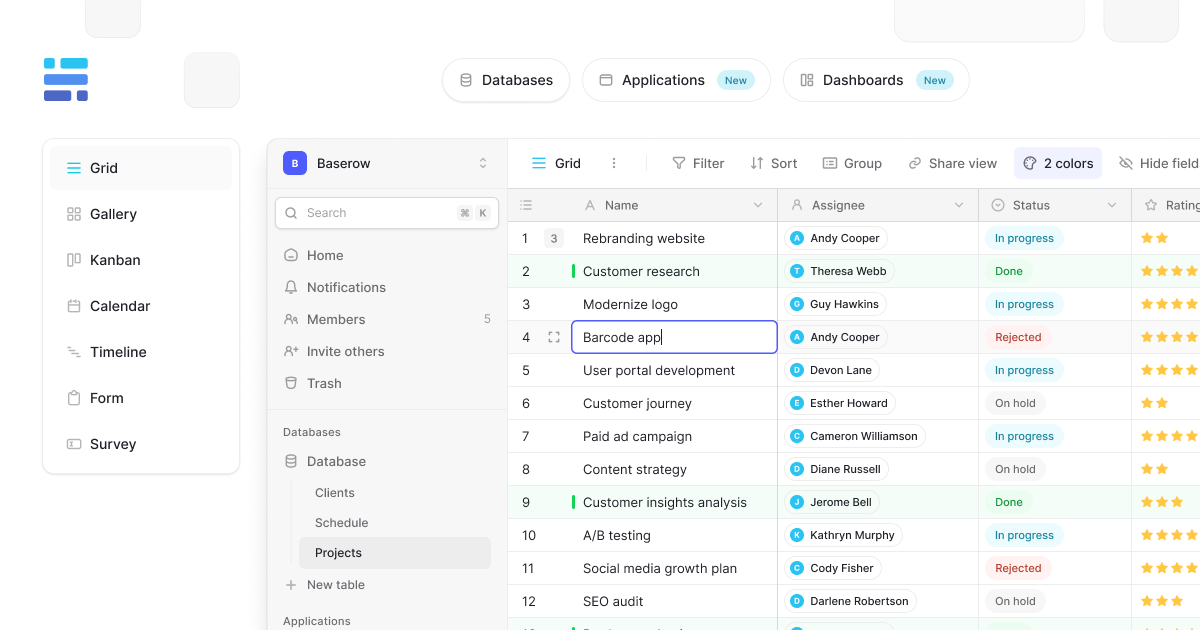
Overview
A Baserow table stores and organizes your data in rows (records) and columns (fields). While tables function like spreadsheets with sorting, filtering, and aggregation capabilities, they go further by displaying the same data in multiple ways; grid, gallery, form, calendar, or kanban.
Tables live inside databases, which live inside workspaces, giving you a clear hierarchy for organizing projects and data.
What makes Baserow tables powerful
Like spreadsheet tabs, tables organize information into rows and columns, while offering multiple views, powerful filtering, and relationship capabilities that spreadsheets can’t match.
| Feature | Traditional spreadsheets | Baserow tables |
|---|---|---|
| Data organization | Single view per sheet | 5+ view types per table |
| Field types | Generic text/numbers | 25+ specialized fields |
| Relationships | Manual lookup formulas | Built-in table linking |
| Collaboration | File conflicts | Real-time editing |
| Data validation | Basic rules | Field-specific validation |
| Customization | Limited formatting | Row colors, field configs |
How tables work in Baserow
Hierarchy structure
To organize with multiple tables, store related but distinct information in separate tables within the same database. For example, a sales database might include:
Workspace (Your company/team)
└── Database (Project or department)
├── Table 1 (Customers – Contact information and company details)
├── Table 2 (Orders – Purchase records linked to customers)
└── Table 3 (Products – Inventory and pricing information)
└── Table 4 (Invoices – Billing documents linked to orders)
Tables contain:
- Rows (records): Individual entries like a customer, order, or task
- Fields (columns): Categories of information like name, date, or status
- Views: Different ways to visualize and interact with the data
- Filters and sorts: Customize what data appears and in what order
Use Link to table fields to connect related information across tables; like linking orders to customers or tasks to projects.
Multiple views, same data
Tables can be visualized in different ways without duplicating information:
- Grid view – Classic spreadsheet layout for detailed editing
- Gallery view – Visual cards perfect for images and media
- Form view – Collect data from external users
- Calendar view – Timeline visualization for dates and events
- Kanban view – Drag-and-drop workflow management
- Timeline view
Common use cases
Business operations
- CRM & Sales: Customer databases, deal pipelines, contact management
- Project Management: Task trackers, sprint planning, team assignments
- Inventory: Product catalogs, stock levels, supplier information
- HR: Employee directories, applicant tracking, onboarding workflows
Teams & collaboration
- Team Check-ins – Track team feedback, suggestions, and project updates
- Product Roadmap – Communicate priorities and strategic plans to stakeholders
Specialized workflows
- Commercial Property Management – Tenant requests, lease tracking, vendor contacts
- Wedding Client Planner – Vendor coordination, budget tracking, event details
- Nonprofit Grant Tracker – Grant deadlines, eligibility, application statuses
Browse 50+ table templates in the template library or import from spreadsheets.
What you can do with tables
Data management:
- Create unlimited rows (records) and fields (columns)
- Import from CSV, Excel, JSON, or XML
- Export data for backups or external use
- Bulk edit multiple rows simultaneously
Organization and filtering:
- Sort by any field (alphabetically, numerically, by date)
- Filter data with complex conditions
- Group rows by categories
- Color-code rows for visual organization
Customization:
- Choose from 25+ field types (text, numbers, dates, files, formulas)
- Configure field properties and validation rules
- Adjust table settings like row height and appearance
- Create personal views for individual workflows
Collaboration:
- Real-time editing with team members
- Row comments and @mentions
- Track changes to see who edited what
- Set permissions to control access
Frequently asked questions
What’s the difference between a database and a table?
A database is a container that holds multiple related tables. For example, a “Sales Management” database might contain “Customers,” “Orders,” and “Products” tables. This hierarchy keeps related data organized in one place.
How many tables can I create in a database?
There’s no hard limit on the number of tables per database. However, keeping tables well-organized improves performance and usability. Most databases work best with 5-15 tables. If you need more, consider splitting into multiple databases or consolidating similar data.
Can I link data between tables?
Yes, this is one of Baserow’s most powerful features. Use Link to table fields to create relationships between tables, like linking orders to customers or tasks to projects. Once linked, you can use lookup fields to display related information and rollup fields to calculate across relationships.
How are tables different from views?
A table stores your actual data (rows and fields). A view is a way to display that data with specific filters, sorts, or visualizations. One table can have multiple views, like a Grid view for editing and a Kanban view for workflow management; all showing the same underlying data.
Can I convert a spreadsheet into a Baserow table?
Yes, import CSV or Excel files directly into Baserow. The import process automatically detects column types and converts them to appropriate field types. After import, you can refine field configurations and add Baserow-specific features like formulas and relationships.
Can I move or duplicate a table to another database?
No, you can export the table as CSV and import it into a new database. Baserow allows you to duplicate within the same database.
Related content
- Create a table – Build tables from scratch or import data
- Create a table via import – Convert spreadsheets to Baserow tables
- Field overview – Learn about available field types
- Table configuration – Customize appearance and behavior
Advanced features:
- Link to table field – Connect related tables
- View customization – Sort and filter your data
- Export tables – Download data for external use
- Delete a table – Remove tables you no longer need
Still need help? If you’re looking for something else, please feel free to make recommendations or ask us questions; we’re ready to assist you.
- Ask the Baserow community
- Contact support for questions about Baserow or help with your account.