Delete and recover data
Baserow protects against accidental data loss with multiple recovery options. Deleted items move to trash for 3 days before permanent deletion, and recent changes can be undone instantly.
This guide covers how to recover accidentally deleted workspaces, databases, tables, fields, and rows using Baserow’s trash system, undo/redo functions, and restoration features.
How data recovery works in Baserow
Baserow provides multiple safety nets to prevent permanent data loss. Deleted items don’t disappear immediately; they’re recoverable through trash (3-day retention), undo/redo (recent actions), and change history (audit trail). Understanding these recovery methods helps you restore data quickly when mistakes happen.
Recovery options:
- Trash - 3-day retention for deleted workspaces, databases, tables, fields, and views
- Undo/Redo - Instant reversal of recent actions like cell edits or row deletions
- Restore popup - 7-second quick recovery notification after deletions
- Row change history: Track row updates
- Change history - Audit log showing who changed what and when (Enterprise)
What can be recovered
Different types of deletions have different recovery options:
| Item deleted | Trash recovery | Undo/Redo | Retention period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workspace | ✓ | ✓ | 3 days |
| Database | ✓ | ✓ | 3 days |
| Table | ✓ | ✓ | 3 days |
| View | ✓ | ✓ | 3 days |
| Field | ✓ | ✓ | 3 days |
| Row | ✓ | ✓ | 3 days |
| Cell value | – | ✓ | Until session ends |
Individual cell deletions don’t go to trash; they can only be recovered via undo/redo immediately after deletion. You can track updates in row history.
Undo and redo actions
Instantly reverse recent changes using Baserow’s undo/redo system. This works for cell edits, row deletions, field modifications, and most table operations.
How to undo/redo
Keyboard shortcuts (fastest method):
- Undo:
Cmd/Ctrl + Z - Redo:
Cmd/Ctrl + Shift + Z
Toolbar buttons:
- Click the undo/redo icons in the bottom-left corner
- Undo reverses the most recent action
- Redo re-applies actions you’ve undone

Quick restore popup
When you delete a workspace, table, row, or make significant changes, a “Restore deleted” popup appears at the bottom of the screen for ~7 seconds. Click Undo in this popup to immediately reverse the deletion.
This quick restore is particularly useful for accidental deletions you notice immediately.
What undo/redo covers
Undo works for:
- Cell value changes
- Row additions and deletions
- Field creations, modifications, and deletions
- View creations and deletions
- Table operations
- Database and workspace deletions
Undo limitations:
- Undo history clears when you close the browser tab
- Some bulk operations may not be fully reversible
- Imports and exports typically can’t be undone
- Changes by other users don’t appear in your undo history
Access the trash
The trash stores deleted workspaces, databases, tables, views, and fields for 3 days before permanent deletion.
Open trash
- Click Trash in the sidebar under Dashboard on the home screen
- The trash displays all deleted items from the past 3 days
- Items show what was deleted, where from, when, and who deleted it
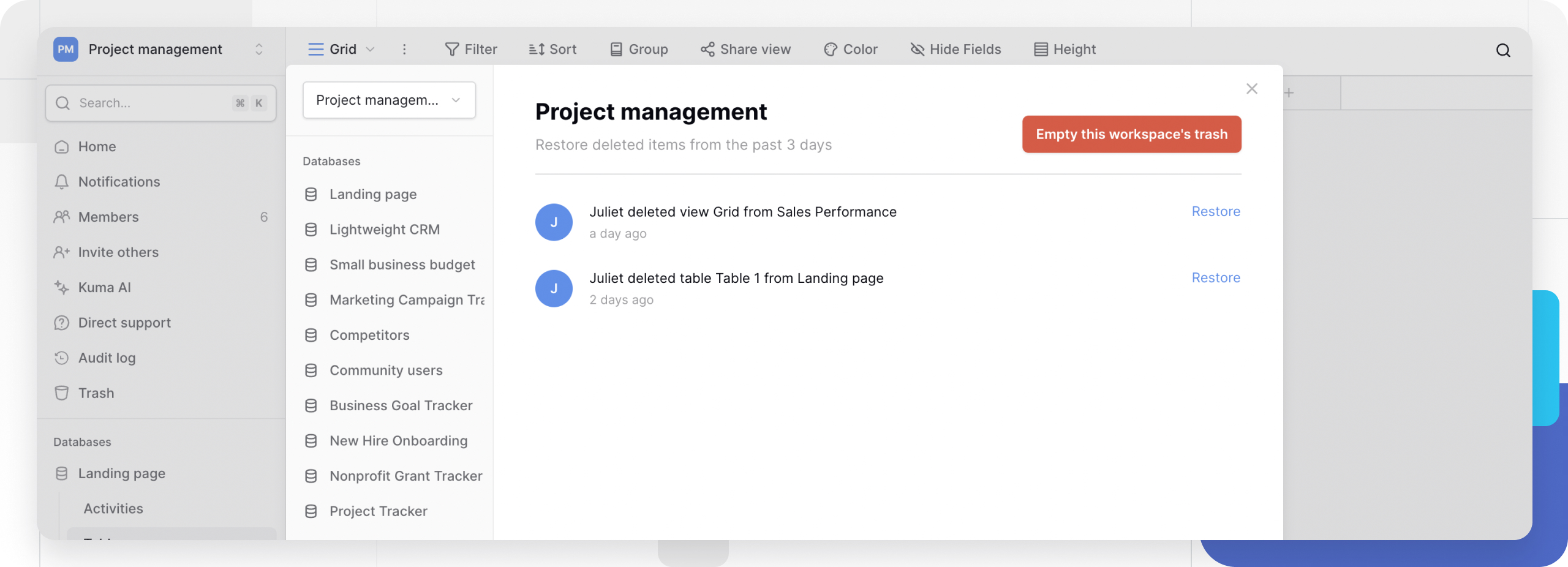
Trash organization
Trash items are organized by workspace. Navigate through workspaces to find deleted databases, tables, views, or fields within each workspace.
Trash displays:
- Deletion timestamp (date and time)
- Item type (workspace, database, table, view, field)
- Original location before deletion
- User who performed the deletion
- Days remaining before permanent deletion
Recover deleted items
Restore items from trash back to their original locations or choose new locations.
Restore from trash
- Click Trash in the sidebar
- Navigate to the item you want to restore
- Click Restore next to the deleted item
- The item returns to its original location immediately
Restored items include all their contents:
- Workspaces restore with all databases, tables, and data
- Databases restore with all tables, views, and fields
- Tables restore with all rows, fields, and views
- Views restore with all configuration and filters
- Fields restore with all column data
Who can restore items
Workspace admins can restore any deleted items from their workspaces, including workspaces, databases, tables, views, and fields.
Members with appropriate permissions can restore items within databases or tables they have access to, but cannot restore entire workspaces or databases.
Learn more: Permissions overview
Restore limitations
After 3 days: Items are permanently deleted and cannot be recovered through trash or any other method. Export important data regularly for long-term backup.
Cell value changes: Modified cell values don’t go to trash; use undo/redo to reverse changes or check change history if available.
Permanently delete from trash
Empty trash to permanently delete items before the 3-day retention period expires. This action cannot be undone.
Empty trash options
Delete individual items:
- Open Trash
- Navigate to the item
- Click Delete permanently next to the item
- Confirm the permanent deletion
Empty entire workspace trash:
- Open Trash
- Navigate to the workspace
- Click Empty this workspace’s trash
- Confirm to permanently delete all items in that workspace’s trash
Warning: Permanently deleted items cannot be recovered by Baserow support or through any technical means. Ensure you don’t need the data before emptying the trash.
When to empty trash
Free up storage: Deleted items count toward storage limits until permanently removed.
Remove sensitive data: Ensure confidential information is truly deleted by emptying trash.
Clean up mistakes: Permanently remove test data or unwanted items created by error.
Before workspace handoff: Clear trash before transferring workspace ownership to prevent new owners from restoring old data.
Deletion workflows by item type
How to delete different items
Delete a workspace - Must be workspace admin. Deletes all databases, tables, and data within the workspace.
Delete a database - Requires database permissions. Deletes all tables, views, and fields within the database.
Delete a table - Requires table permissions. Deletes all rows, fields, and views within the table.
Delete a view - Deletes view configuration but not underlying table data.
Delete a field - Permanently removes the field and all data in that column.
Frequently asked questions
What happens after the 3-day trash retention period?
Items are permanently deleted from Baserow servers and cannot be recovered through any means, including by Baserow support. The 3-day period is absolute; there’s no extension or grace period beyond this. Export important data before deletion or regularly for backup purposes.
Can workspace admins see who deleted items?
Yes. The trash displays the username of who deleted each item along with the deletion timestamp. This audit trail helps track accidental deletions and identify training needs.
Does trash count toward my storage limit?
Yes. Items in trash count toward workspace storage limits until permanently deleted or until the 3-day retention period expires. If you’re approaching storage limits, consider emptying trash to free up space.
Can I restore individual fields from a deleted table?
Yes, but you must restore the entire table first. Once the table is restored, you can then work with individual fields. You cannot restore individual fields without restoring their parent table.
What happens to linked data when I restore items?
Link-to-table fields and relationships restore correctly when you recover items. If you deleted and restored both linked tables, connections re-establish automatically. If one linked table was permanently deleted, the link fields become empty.
Can I undo actions by other users?
No. Undo/redo only works for your own actions in your current browser session. You cannot undo changes made by other workspace members. Workspace admins can use trash to restore items deleted by others or check change history to see who made what changes.
Is there a way to back up data beyond the 3-day period?
Yes. Export tables, export views, or export entire workspaces regularly to create backups. For automated backup solutions, consider using the Baserow API or webhooks with external backup systems.
Can I recover an element (like a button, text, or container) after deleting it?
Currently, when you delete an individual element or container within the Baserow Application Builder, it is permanently removed and cannot be recovered.
Unlike deleting an entire Application or Database, which moves to your Workspace Trash Bin for 3 days, individual elements are not yet supported by the Trash Bin system.
Related resources
Deletion guides
- Delete a workspace - Workspace deletion and requirements
- Delete a database - Database removal process
- Delete a table - Table deletion steps
- Delete a view - View removal
- Delete a field - Field deletion
Data management
- Export tables - Download table backups
- Export views - Export filtered data
- Export workspaces - Complete workspace backups
- Import data - Restore exported data
Access control
- Permissions overview - Who can delete and restore
- Manage workspace members - Control access levels
Audit and tracking
- Row change history - Track data modifications
- Notifications - Get alerts for workspace changes
Advanced features
- Database API - Programmatic backups
- Webhooks - Automate backup workflows
- Snapshots - Point-in-time backups (Enterprise)
Still need help? If you’re looking for something else, please feel free to make recommendations or ask us questions; we’re ready to assist you.
-
Contact support for questions about Baserow or help with your account
- On this page
- How data recovery works in Baserow
- What can be recovered
- Undo and redo actions
- Access the trash
- Recover deleted items
- Permanently delete from trash
- Deletion workflows by item type
- Frequently asked questions
- What happens after the 3-day trash retention period?
- Can workspace admins see who deleted items?
- Does trash count toward my storage limit?
- Can I restore individual fields from a deleted table?
- What happens to linked data when I restore items?
- Can I undo actions by other users?
- Is there a way to back up data beyond the 3-day period?
- Can I recover an element (like a button, text, or container) after deleting it?
- Related resources